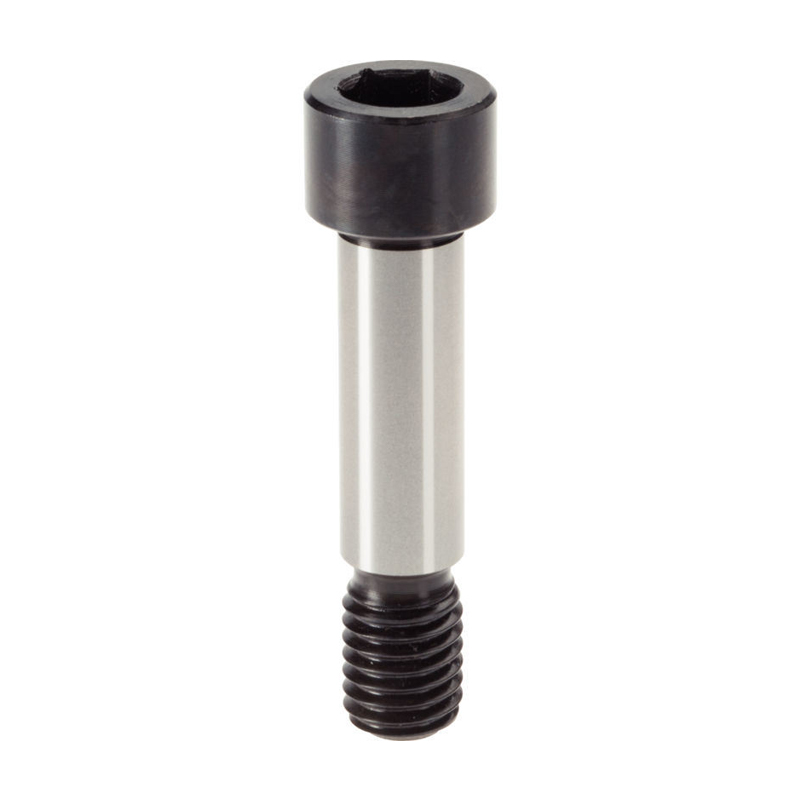
What is a 12.9 grade shoulder bolt?
A 12.9 grade shoulder bolt, also known as a shoulder screw or hexagon socket shoulder bolt, is a high-precision fastener with a smooth shoulder and partial threads, specifically designed for high-strength and precision motion applications.
Features
Structural features
The 12.9 grade shoulder bolt consists of three key parts:
Bolt head: commonly with internal or external hexagonal design, which is convenient for high torque installation and removal.
Smooth shoulder: precision machined to ensure stability of rotating or sliding parts.
Threaded end: partially threaded design to ensure a secure fixation and improve load-bearing capacity.
Core Features
Ultra-high strength: alloy steel (such as 42CrMo) with tensile strength ≥1220MPa is used to ensure reliability in high-load applications.
Precision tolerance: shoulder diameter, length, and coaxiality are strictly controlled to ensure precise positioning and sliding fit of mechanical parts.
Wear-resistant and durable: the surface is quenched, blackened, phosphated or nickel-plated to improve wear resistance and corrosion resistance.
High torque performance: It can withstand higher tightening torque and is suitable for heavy machinery and high dynamic load environments.
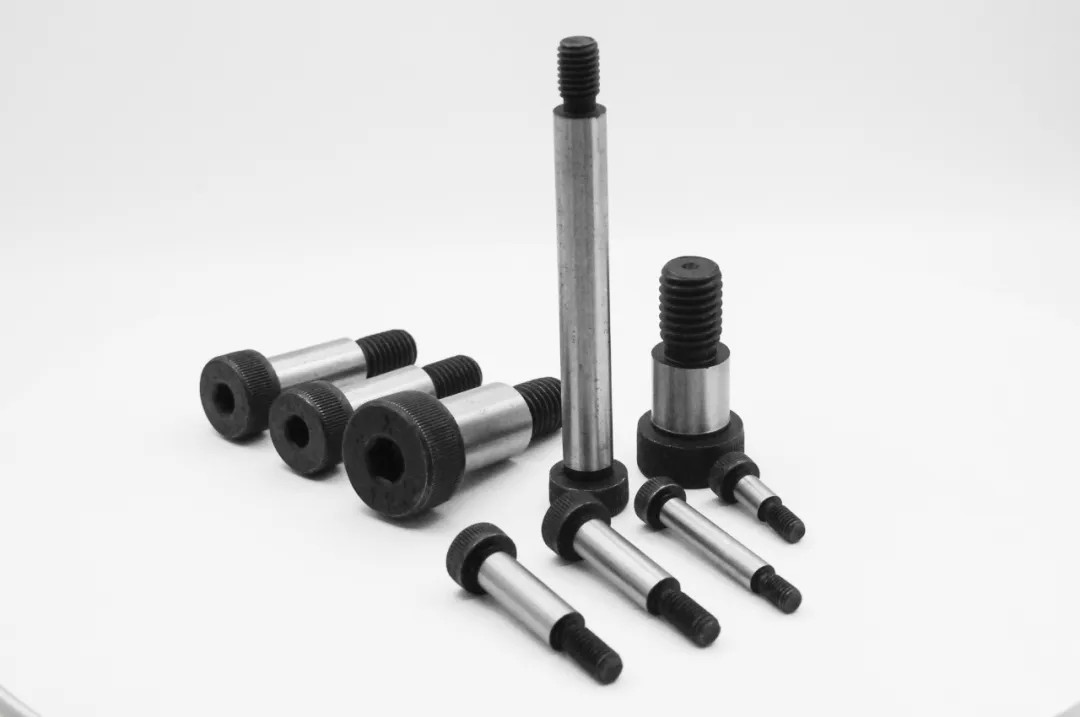

Application scenarios of 12.9 grade shoulder bolts
Due to its high strength, precision processing and motion adaptability, 12.9 grade shoulder bolts are widely used in multiple industries, especially in scenarios with high load and high precision requirements.
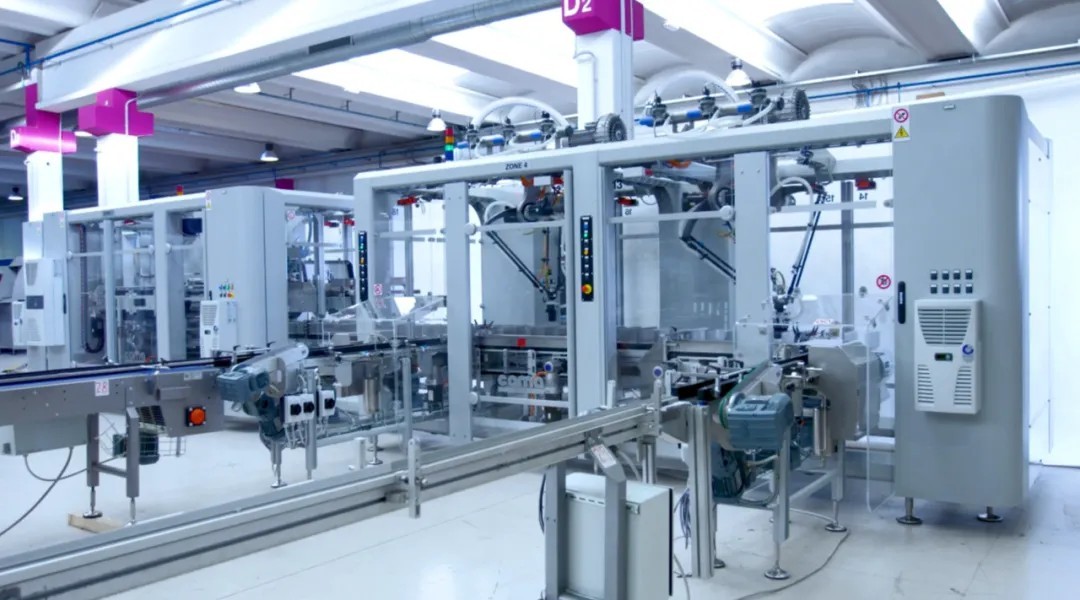

Mechanical equipment
In automated machinery, precision machine tools and production line equipment, shoulder bolts are used to support and slide components to ensure smooth operation of the equipment.
Slide rails and guide mechanisms: ensure the accuracy of linear or rotational motion.
Transmission system: used as connecting rod and bearing seat fixing bolts to reduce wear on moving parts.
Fixtures and tooling: fixed positioning clamping devices to improve production accuracy.
Mold manufacturing
Injection mold: used for sliders, guide plates, and positioning mechanisms to ensure smooth opening and closing of the mold.
Stamping mold: used for guide pin fixation and slider components to improve mold life and accuracy

Automotive Industry
12.9 grade shoulder bolts are widely used in engines, suspension systems and brakes in automobile manufacturing.
Engine components: connect rocker arms, connecting rods, and valve mechanisms to ensure stability during high-speed operation.
Suspension system: withstand high-frequency vibration and impact forces at the connection points of shock absorbers and swing arms.
Braking system: used for brake calipers and sliding guides to provide high temperature resistance and high load capacity.

Electronic and automation equipment
Robot joints: used as rotation axes to ensure precise positioning and flexible movement of robotic arms.
Automated assembly lines: used for sliders and guides to improve equipment stability and accuracy.

Aerospace
Flight control system: used to control the rotation and connection components of control surfaces and flaps.
Satellite manipulator: provides high-precision rotation fulcrum to ensure stability and reliability.
Medical equipment
X-ray machines, CT scanners: used for slide rails and moving parts to ensure accurate operation of the equipment.
Surgical robots: used for robot arm joints to ensure precise control and stability.
Manufacturing process of 12.9 grade shoulder bolts
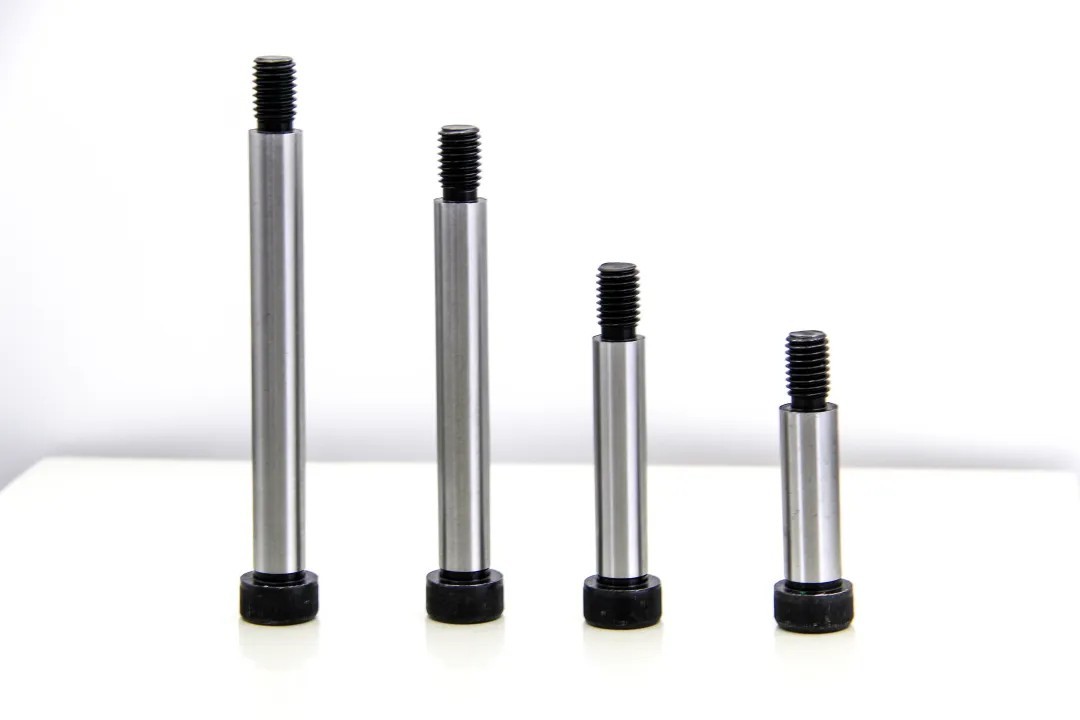

1.Main materials
Common materials for 12.9 grade shoulder bolts include:
42CrMo (alloy steel): high strength, good wear resistance, suitable for high load applications.
SCM435 (chrome-molybdenum steel): good toughness and fatigue resistance, suitable for impact load environments.
Stainless steel (304, 316L): corrosion resistant, but low strength, mostly used in food and medical equipment.
2.Production process
Material cutting: Precise cutting of high-strength steel bars.
CNC precision machining: Turning of bolt heads, shoulders and threaded parts to ensure strict tolerances.
Thread machining: Rolling threads are used to improve strength and fatigue life.
Heat treatment: Quenching + tempering to improve hardness and wear resistance.
Surface treatment: Galvanizing, blackening, phosphating to enhance corrosion resistance.
Quality inspection: Three-coordinate measuring instrument, hardness test, torque test are used to ensure high precision and consistency.
Corrosion, but the strength is low, mostly used in food and medical equipment.
3.Industry Standards
The production of shoulder bolts must comply with international standards to ensure their performance and reliability.
ISO 7379: Standard for dimensions, materials and tolerances of metric shoulder bolts.
DIN 923: German standard, widely used in the European market.
ASME B18.3: Specification requirements for American shoulder bolts, suitable for the North American market.
JIS B 1180: Japanese standard, used in precision machinery manufacturing.
These standards specify shoulder diameter, length tolerance, thread specifications, tensile strength and surface treatment to ensure the stability and compatibility of bolts in harsh environments.
4.How to choose the right shoulder bolt?
When choosing a shoulder bolt, you need to consider the following factors:
Load requirements: determine the required tensile strength and fatigue life.
Shoulder size: ensure the compatibility with sliding or rotating parts.
Thread specifications: choose metric or imperial threads suitable for the equipment.
Surface treatment: choose anti-corrosion coatings such as galvanizing, blackening, phosphating, etc.
12.9 grade shoulder bolts are essential in mechanical equipment, automotive manufacturing, molds, automation and aerospace due to their high strength, precision tolerances and adaptability to dynamic movement. Its strict manufacturing standards and excellent performance make it a core product in the high-end fastener market.
Have you used 12.9 grade shoulder bolts in your industry? Welcome to share your experience!









